
by Legalnaija | Feb 1, 2024 | Blawg

Aviation law concept. Judge gavel and airplane on blue background. Flight cancellation
Disputes are inevitable in our day to day life especially in business and in the social strata of the society. It is pertinent to state that there are numerous benefits of using an arbitrator in handling civil aviation disputes which allows the disputing parties to make a choice on having a neutral third party to hear their case and pass an award. exploring this mechanism is helpful where the parties have a history of conflict or a risk of bias.
The aviation sector is a sensitive sector of any nation, it is very sensitive because of the high cost of running the sector. arbitration can be used to resolve complex or technical disputes. disputes in aviation are complex and technical in nature. the areas where the disputes mainly spring from aircraft design or maintenance. when legal disputes arise in this areas mentioned, it is important to understand that merely proving that the aircraft design was the probable reason for the accident/injury is not adequate as there are factors to consider like that of the misuse of the aircraft by the pilot, the preliminary presentation of risk by the aircraft design, and other similar factors.
The factors which are to be taken into consideration regarding disputes in the civil aviation sector vary completely. In respect of the issue of maintenance in a legal dispute it is worthy to mention that to comprehend that maintenance becomes necessary to ensure that the novel structure and materials employed for the better operation of the aircraft are carried out smoothly and are not incurring losses if the structure, parts are always malfunctioning. The following are inspections, repair processes and various maintenance programs. the manufacturers of these parts of the aircraft and the companies buying these aircraft are regarded as the same. The result of this is that disputes are bound to arise in the case of malfunctioning of the aircraft/parts of the aircraft.
On the issue of handling aviation disputes by arbitration, an arbitrator who is considered to handle civil aviation dispute resolution and passing an award when he or she has been selected, several factors should be considered when choosing. The main point to consider in choosing is to select an arbitrator who is familiar with the civil aviation sector. The reason is because the arbitrator will need to be able to understand the complex issue that may be involved in the dispute. again, it is adequate to choose an arbitrator who is neutral and impartial. the arbitrator must not have any personal interest in the outcome of the case. and finally, in the choice of an arbitrator the point is that the arbitrator should have experience in arbitration. This is because the arbitrator will need to be able to handle the complex legal issue that may arise during the arbitration. Apart from the arbitrator, all related persons have roles to play in the Civil Aviation process such as, mediators, parties, lawyers and experts.
In conclusion, the role of civil aviation arbitration in resolving disputes in the aviation sector is crucial, it provides a forum for the parties to resolve their differences without resorting to litigation. this is also important for promoting industry wise stability and growth.

by Legalnaija | Dec 28, 2023 | Uncategorized

Are you looking for a way to enhance your legal skills, knowledge, and career prospects? Do you want to learn from the best experts in the field, at your own pace and convenience? Do you want to access a rich library of courses and videos, on various topics related to law and practice?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, then you need to check out the Lawlexis page on Selar. You can stream hours of professional training content for lawyers of all levels and backgrounds. Whether you are a student, a junior associate, a senior partner, or a solo practitioner, you will find something useful and relevant for your needs and interests.
Lawlexis International covers a wide range of subjects, such as:
– Film & Media Contracts
– Startup Compliance
– Negotiation & Dispute Resolution
– Startup Funding
– And much more!
You can stream the content anytime, anywhere, on any device, with a simple payment as low as 2,500 Naira. At Lawlexis we have provided training courses to over 500 lawyers, and we are excited to offer videos of our training sessions to help build the capacity of lawyers across Nigeria.
Don’t miss this opportunity to join the Lawlexis community and access the best legal content available online. To get started, visit the Lawlexis selar page at https://selar.co/m/lawlexis-international1 and sign up today. You won’t regret it!
@Lawlexis

by Legalnaija | Dec 22, 2023 | Uncategorized

DRIVE INCREASED FOREIGN DIRECT INVESTMENT INTO NIGERIA USING ARBITRATION- TOLU ADEREM
Arbitration experts in Nigeria have called for a stronger commitment to foreign direct investment and the enforcement of arbitral awards in the country. This call was made at the 2023 Annual Dinner of the International Law Association (ILA), Arbitration Commission, held in Lagos State. The theme of the dinner was ‘International Arbitration: Putting Our House In Order’.
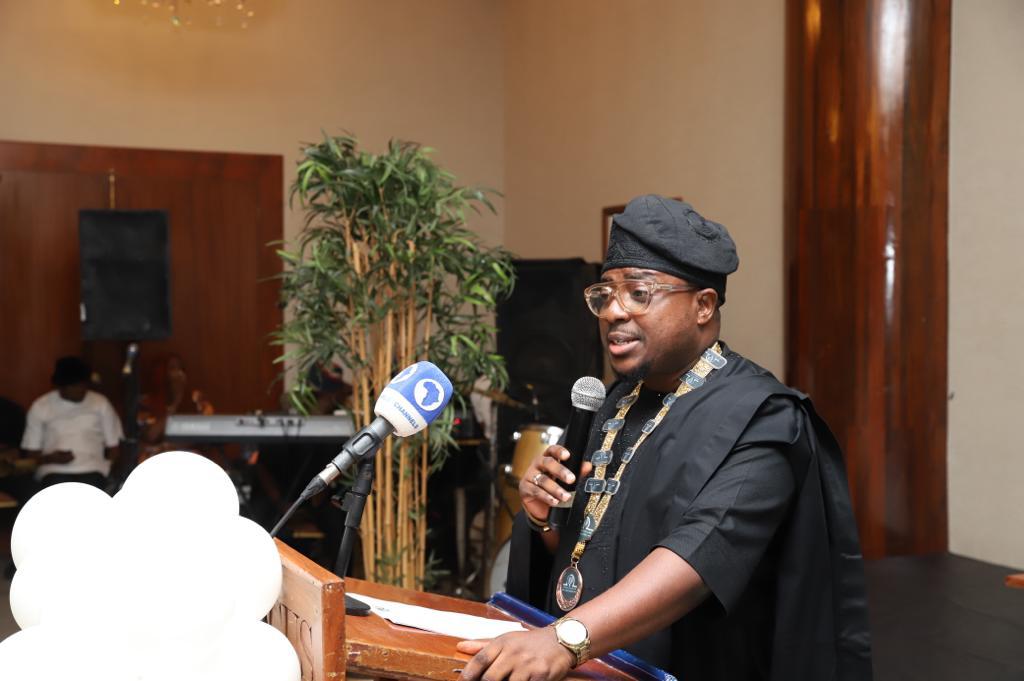

Leading this charge, Prof. Tolulope Aderemi, Chairman of the Arbitration Committee, expressed concerns about the increasing number of appeals on arbitration-related matters reaching the Supreme Court. He emphasized the need to reconsider such appeals on weak grounds, as they hinder Nigeria’s potential as a preferred foreign investment destination. Aderemi also called for strict penalties to be imposed on those who violate the ethics of the industry.
Aderemi urged his colleagues to continue to practice arbitration with integrity and within ethical boundaries. He proposed the establishment of a national code of ethics for arbitrators, the evaluation of legal provisions relating to misconduct, and the enhancement of accountability and probity in the conduct of arbitrators. He also called on the Nigerian government to conduct an audit of contracts similar to the P&ID contract to assess the government’s exposure and mitigate risks.
Prof Damilola Olawuyi, SAN, President of the International Law Association, Nigerian Branch, commended the efforts of the Arbitration Committee in leading change in the Nigerian arbitration landscape. He emphasized the importance of aligning arbitration practices in Nigeria with international best practices and standards.
The keynote speaker, Mr. Babatunde Fagbohunlu, SAN, discussed the challenges faced by African arbitrators in accessing the global arbitration market and the significant arbitral awards against the Nigerian government. Fagbohunlu emphasized the need for Nigerian arbitrators to equip themselves for global opportunities. He proposed the establishment of a single arbitration institution for the African continent to enhance its attractiveness and participation in international arbitration. Fagbohunlu also stressed the importance of supporting the judiciary in enforcing arbitration agreements and awards.
During the Fireside chat, Mrs. Hairat Balogun, a Life Bencher and the first female Attorney General and Commissioner for Justice, Lagos State, addressed the ethical issues within the legal profession. She attributed the decline in the profession’s standing to the lack of adherence to ethical rules and the diluted training of lawyers. Balogun criticized the current method of admission into the Nigerian Law School and called for a reconsideration of the suggestion to admit only students from accredited schools.
The 2023 ILA Dinner concluded with a unanimous recognition of the need for practitioners to uphold integrity, accountability, and probity in arbitration. The event highlighted the importance of attracting foreign direct investment and enforcing arbitral awards in Nigeria. The discussions emphasized the role of arbitration in economic development and the need for practitioners to practice with diligence and integrity to support governments worldwide.

by Legalnaija | Dec 22, 2023 | Blawg

Are you looking for the best books and accessories for lawyers? Do you want to publish your own legal book and get it marketed by experts? Do you need to buy outfits that suit your professional style and budget?
If you answered yes to any of these questions, then you need to check out Princess Legal World!
Princess Legal World is a one-stop shop for all your legal needs. We offer a wide range of books, from textbooks and case studies to biographies and novels, all written by renowned authors and experts in the field. Whether you are a student, a practitioner, or a enthusiast, you will find something that interests you in our collection.
We also sell high-quality accessories for lawyers, such as pens, notebooks, briefcases, mugs, and more. These items are designed to make your work easier and more enjoyable. You can also personalize them with your name, logo, or motto.
But that’s not all. Princess Legal World also helps aspiring authors to publish and market their own legal books. We finance the production of new books and provide editorial and promotional support. We have a network of distributors and retailers who can help you reach a wide audience and earn royalties.
And if you are looking for outfits that match your professional image, you will love our clothing line. We have suits, dresses, shirts, skirts, and more, all made from high-quality fabrics and tailored to fit you perfectly. You can also choose from different colors, patterns, and styles. And the best part is, we offer bulk sales of our outfits at a highly discounted rates.
So what are you waiting for? Visit Princess Legal World today and discover the amazing products and services we have for you. You will be glad you did!
See flyer for more details!

by Legalnaija | Dec 6, 2023 | Blawg
In Nigeria, it is a statutory requirement for all businesses, private limited companies, and trustee organisations to file annual returns every year. This is in accordance with the Companies and Allied Matters Act (CAMA) 2020, which states in Chapter 16 that all companies in Nigeria must submit the prescribed form with the necessary information to the Corporate Affairs Commission (CAC).
The only exception is companies with one member, which are exempted from filing annual returns according to Section 421 (2) of CAMA 2020. Newly incorporated companies have 18 months from incorporation to submit their first annual returns, while established companies must file their returns within 42 days of their annual general meetings. Therefore, it is necessary for companies in Nigeria to file their annual returns on a yearly basis.
Importance of filing annual returns
The filing of Annual Returns is an essential part of business operations. It is necessary for companies to stay current with their post-incorporation services from the CAC such as filing for Certified True Copies (CTC) of Incorporation documents, increasing share capital, making changes to business objects or registered addresses, and changes to directors, partners, or trustees. Filing Annual Returns on time and paying any applicable penalties in full is required to receive any post-incorporation service from the CAC.
Furthermore, the majority of contractual bids in public or private sectors usually require an up-to-date yearly report from the entity as a major pre-requisite for compliance. It is essential for companies to keep their records updated in order to satisfy this obligation.
Annual Returns also serve to inform the Commission of a company’s ongoing existence, referred to as a ‘going concern’, and keep the company’s name on the CAC register. Additionally, a business that is fully compliant and up to date with its Annual Returns will be able to demonstrate trustworthiness during due diligence checks with CAC, allowing investors to quickly and confidently obtain information about the company.
In conclusion, filing Annual Returns is a vital factor in ensuring a company’s post-incorporation services are processed in a timely manner and that the company is seen as a reputable entity.
Implications of failing to file your annual returns
The implications of not following the law when it comes to filing annual returns are outlined in Section 425 of CAMA 2020. This provision stipulates that companies and their directors or officers may face a penalty at the discretion of the Commission. In addition, the Commission is empowered to delist a company from the Register of Companies if it fails to file yearly returns for a period of ten years. This is based on the presumption that the company is inactive.
Those who disagree with the removal of the company’s name from the register may appeal to the court at any time before the expiration of 20 years from the date of the notice of removal, on the condition that the court is convinced that the company was indeed operating at the time of the striking off. To make such an appeal, a formal letter must be written to the CAC’s Registrar General (RG), detailing the reasons why the annual return was not filed on time. Supporting documents such as all payable dues and updated company records must also be provided. If the application is accepted, a relisting certificate will be issued to the company.
 Olamide Oyetayo
Olamide Oyetayo
The information provided in this article aims solely to educate readers generally. It does not establish an attorney-client relationship with our law firm or constitute legal counsel. Please contact us directly for any specific legal assistance required.

by Legalnaija | Dec 2, 2023 | Book

Black Friday Deals & Exciting Offers For You.
Happy new month to all our subscribers! We are grateful for your continued support and patronage of our platform. We have been working hard to provide you with the best legal services and information in Nigeria.
This month, we have some exciting news and offers for you. To celebrate the new month, we are extending our 50% discount on the yearly subscription to the first 100 subscribers who renew their subscription. This is a limited time offer, so hurry and subscribe now. Sign into your dashboard here app.legalnaija.com
But wait, there’s more! We have another amazing offer for you. Our bookstore is having a Black Friday sale that you don’t want to miss. You can get up to 80% off on selected books and publications from our collection. Whether you’re looking for textbooks, journals, casebooks, or magazines, we have something for you. You can browse our bookstore and order online from the comfort of your home. The sale ends on January 5th, so don’t delay. Visit the shop here legalnaija.com/store
We look forward to hearing from you and serving you better. Happy new month once again! 🎉🎉🎉

by Legalnaija | Nov 25, 2023 | Uncategorized
ESG Due Diligence in Nigerian Commercial Transactions
A traditional due diligence (DD) is performed to verify details in a transaction and detect potential defects in a deal or investment prospect. This process would usually include considerations of environmental, health, and safety (EHS) issues.
However, given the increasing emphasis on sustainability by stakeholders and regulatory bodies, it has become imperative to integrate Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) metrics into the due diligence procedures to steer clear of bad investments.
Consequently, investors are now inclined to allocate higher financial resources for sustainable targets. Unlike the relatively narrower scope of EHS, ESG introduces a more comprehensive array of sustainability risks and opportunities directly influencing transaction valuation.
Investors and creditors are increasingly employing Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) criteria to evaluate risks and opportunities for value creation. Businesses now face mounting pressure from various sources, including regulatory bodies, investors, and local communities, compelling them to adopt a proactive stance on ESG issues.
As said above, while the due diligence process traditionally encompassed Environmental, Health, and Safety (EHS) considerations, there’s a discernible shift toward a more comprehensive review utilizing ESG standards that span environmental, social, and governance topics. This shift is propelled by heightened expectations from stakeholders and growing concerns about the climate and environmental impact of business activities. In commercial transactions such as Mergers and Acquisitions (M&A), the integration of ESG due diligence is crucial during the negotiation phase, as significant ESG findings can exert a tangible influence on the valuation of the target company.
Conducting ESG due diligence serves several key objectives within the context of commercial transactions. Primarily, it aims to comprehensively grasp the risk profile and exposure of the company to environmental, social, and governance (ESG) considerations. This process involves a detailed examination of associated ESG risks and the identification of any red flags that may arise during the due diligence process. Additionally, it aims to ferret potential risk mitigation measures.
Given that a company’s ESG performance significantly influences its operations (its capacity to secure financing, maintain employee satisfaction and morale, capitalize on growth opportunities, and retain and expand its customer base), ESG considerations become crucial in decision-making. As a result, stakeholders such as investors, employees, customers, regulators, and others are increasingly holding companies accountable for their ESG practices.
In a comprehensive survey covering Europe, the Middle East, and Africa, a 2022 KPMG study found that over two-thirds of dealmakers expressed a readiness to offer a premium for a target exhibiting advanced ESG maturity in alignment with their specific ESG priorities.1 In another survey of 200 ESG practitioners including corporate investors, financial investors, and M&A debt providers, it was found that 74% of professionals are already integrating ESG considerations as part of their M&A agenda, with the identification of ESG risks and opportunities given as the top reason for conducting ESG due diligence, by 46% of respondents, followed by requirements by investors, cited by 19%, and preparation for regulatory requirements by 14%.2
Evaluating a company’s environmental, social, and governance (ESG) practices through due diligence provides insights into its value creation and sustainability. Beyond assessment, this process empowers investors to anticipate and implement post-closing strategies to mitigate identified risks. Investors often place a premium on sustainable targets, driven by the belief in a positive, long-term relationship between sound ESG practices and financial returns. Essentially, strong ESG performance is considered a proxy for effective management, recognizing its pivotal role in determining a company’s financial value.
Materiality
Determining which ESG activity to scrutinize might be taxing because ESG is a broad term. I liken it to a skilled fisherman navigating the open sea. ESG, akin to a boundless ocean, teems with various sea monsters representing diverse aspects. Much like a fisherman’s cautiousness deepens with the water’s depth, the scrutiny of ESG factors intensifies depending on the specifics of the transaction and the nature of the company involved.
Close to the shore, where waters are shallower, a fisherman may only concern himself with a few threats. Similarly, in the realm of ESG, the level of scrutiny hinges on the subject of the transaction. ESG, being extensive and at times complex, encompasses different topics under each pillar. For instance, within the Environmental (E) pillar, considerations span biodiversity, climate change, decarbonization, air pollution, deforestation, water contamination, and more. The Social (S) pillar addresses matters such as minimum wage, child labor in the value chain, cybersecurity, data privacy, diversity and inclusion, and human rights. Governance (G) encompasses business ethics, corporate governance, responsible tax records, regulatory compliance, and anti-corruption measures.
During negotiations, it is evident that not all these issues would be equally applicable. Identifying the pertinent (material) ESG topics for scrutinizing a transaction represents the initial and significant challenge. There is no one-size-fits-all approach; hence, the scope of an ESG due diligence must be tailored on a case-by-case basis, considering the unique sustainability-related risks and opportunities associated with each transaction.
Nigeria
The Financial Reporting Council of Nigeria’s recent emphasis on sustainability risk disclosures, coupled with the proposal for a carbon tax and the escalating concerns about data privacy from both stakeholders and regulators, reflects a notable shift towards more rigorous ESG regulatory practices in Nigeria. This shift underscores the importance of conducting thorough ESG due diligence. Investors and financiers adopting ESG due diligence procedures enhance their readiness to navigate evolving regulatory requirements.
Incorporating ESG due diligence into the deal process not only distinguishes organizations in a competitive field but also positions them to secure deals successfully. This strategic approach demonstrates a commitment to long-term value creation, providing investors with a competitive advantage. Also, prioritizing ESG due diligence ensures a comprehensive understanding of the broader spectrum of sustainability risks and opportunities directly influencing deal valuation.
While ESG considerations have been around for many years, ESG due diligence is still a relatively new concept at its nascent stage of adoption. As a result, there is no uniform standard or guideline for organizations to comply with. The good news is organizations can develop their ESG due diligence template or framework aligned to their unique business needs.
It’s essential, however, for an organization to already have an established ESG strategy as a prerequisite for building a robust ESG due diligence framework. Before delving into the specific ESG considerations relevant to a transaction, it’s crucial to evaluate the ESG priorities that will shape decision-making processes. Subsequently, the ESG strategy can be seamlessly connected to the ESG due diligence process, enabling the development of a tailored ESG due diligence framework for the deal at hand.
I agree, it is not as easy as it sounds – condensing a practical concept into words is a trap for ridiculous simplification. Nonetheless, I’ve managed to deconstruct the concept into its prime elements. It is crucial to underscore that ESG due diligence casts its net over all entities involved in a transaction. Also, undertaking conventional financial due diligence while neglecting non-financial facets such as ESG is akin to disregarding factors that may become legal and financial risks in the long run (See FTX, Binance, OpenAI, Terra, Gemini Trust and BlockFi). ESG considerations wield the power to either fortify, erode, or forge value. Investors sidestepping ESG due diligence do so at their own peril.
Source: www.linkedin.com/peterokediya

by Legalnaija | Nov 7, 2023 | Blawg, Book

Hey Counsel! We’re excited to announce our latest campaign where you get a free mobile accessory by buying books worth N45,000 or more on the Legalnaija Bookstore.This is a great opportunity to get your hands on some of the latest accessories for your mobile device.
To participate, all you have to do is make a purchase of N45,000 or more on the Legalnaija Lawyers. Once you’ve made your purchase, you’ll automatically receive a free mobile accessory alongside your books. It’s that simple!
Accessories include chargers, phone stands, Bluetooth keyboards, earphones and more. This campaign will end on November 31st, 2023, so don’t miss out.
So what are you waiting for? Head over to Legalnaija.com/store today, where we have over 150 lawbooks in different areas of law, and start shopping. Not only do you get to update your law library with the latest books but you also get a brand new mobile accessory!
www.legalnaija.com/store
@Legalnaija
+2349029755663
#lawbooks #legalnaija #mobileaccessories #kakusiga #lawbooks #lawaccessories #legal #lawyers #nigerianlawyers #legalnaijabookstore #instagramlawyers #lawyersbookstores

by Legalnaija | Nov 7, 2023 | Blawg
The decision of the London Commercial Court in the case of Process & Industrial Development (P&ID) v Federal Republic of Nigeria, coram Knowles J, handed down on October 2023, has garnered significant global attention within the legal and international business communities. Its consequences have questioned the seeming usefulness of arbitration as a dispute resolution mechanism casting a shadow on the potential corruption of arbitrators, deliberating the various perspectives surrounding this case.
The judgment has been welcomed by several distinguished arbitration practitioners (particularly from Nigeria) and even non-practitioners. Whilst the delight may be in order, sight must not be lost of the lessons to be learned from some key pronouncements (which may be obiter dictum) made by the court, which must necessarily generate a retrospection.
Background
In the year 2010, P&ID executed a Gas Supply and Processing Agreement (GSPA) with Nigeria’s Ministry of Petroleum Resources. This agreement required Nigeria, via the Ministry of Petroleum Resources, to deliver natural gas (“wet gas”) to P&ID, which would process it into “lean gas” at no cost to Nigeria. The crux of the matter began to unfold when Nigeria failed to supply the wet gas in breach of its obligations under the GSPA and P&ID also, consequently, failed to perform its corresponding obligations.
In August 2012, P&ID initiated the arbitration process per the terms of the GSPA, claiming damages resulting from Nigeria’s alleged breach. The arbitration, conducted under the rules of the (then) Nigerian Arbitration and Conciliation Act, comprised Sir Anthony Evans, Chief Bayo Ojo, SAN, and Lord Hoffmann (as Chairman)-two highly respected English jurists and an Attorney General of Nigeria. It was held in Nigeria and adhered to Nigerian law.
The tribunal sat for over three years, and in January 2017, awarded P&ID damages proposed to be $6.597 billion, calculated based on the commercial expectation of P&ID, over the twenty-year lifespan of the GSPA. This figure, however, escalated considerably due to the application of the English pre-and post-judgment interest rates, thereby accruing to an immense sum of $9.6 billion by the summer of 2019.
In a move to enforce the terms of the arbitral award, the company sought to enforce the arbitration award in a London Commercial Court. This made Nigeria challenge the award on the grounds of fraud and corruption surrounding the contract’s creation and performance and the impartiality of the tribunal. In September 2019, the UK court granted Nigeria permission to appeal the award.
As far as the Nigerian government was concerned, the Tribunal’s decision was an ‘economic warfare’ that influenced foreign direct investment, and the international perception of doing business in Nigeria, and cast a shadow over the image of contractual fairness in Nigerian commercial sectors.
In confirming the initial award of $6.6 billion, followed by a later increment to an outstanding $10 billion in favor of P&ID, Justice Butcher placed Nigeria in a precarious financial situation. This seismic judgment sent shockwaves throughout the Nigerian state, already grappling with enormous economic challenges. This is due to its enormous financial implications accruing heavy interests per day and also questioning the sincerity and transparency of public officials in contract negotiations and enforcement.
In light of such overwhelming fiscal implications, Nigeria appealed the judgment. Justice Knowles of the English Commercial Court was charged with sitting over the appeal. In this case, Justice Knowles permitted Nigeria to extend the time to bring its challenge against the arbitral award. His decision was fundamentally based on the prima facie evidence presented concerning fraudulent and corrupt practices during the contract signing and execution, which implies that the contract should be nullified or reconsidered. This precedent-setting ruling necessitates a recalculation of how arbitration cases involving states and corporations are adjudicated in the international legal community.
To Nigeria, Justice Knowles’ ruling is a significant lifeline. Considering Nigeria’s current economic condition, amidst recovering from the 2020 global economic downturn and a dwindling oil market, a $10 billion payout would undoubtedly strain the nation’s budget vastly.
Simultaneously, Justice Knowles’ judgment carries multilayered implications for the international arbitration community. While serving as a sobering reminder to ensure strict adherence to ethical guidelines in contract negotiations, his ruling insinuates a possible shift in arbitration norms within the legal fraternity. The emphasis on fraud and corruption as key considerations in arbitral decisions could impact future arbitration rulings, sparking a pivoting focus on transparency and corporate governance; particularly now that Nigeria’s Arbitration and Mediation Act, has deleted the reference to misconduct, as a ground for setting aside an award.
However, the ruling also raises questions about the sanctity of arbitral awards and predictability in international arbitration. It prompts the query if award creditors can rely on arbitration awards, especially when there is a suspicion of fraud or corruption that was not initially uncovered during the process of arbitration. Moreover, it places an additional burden on arbitral tribunals to investigate and consider allegations of corruption during arbitrations.
In sum, Justice Knowles’ judgment is historic. Its repercussions ripple throughout the Nigerian state and beyond, fundamentally shaking the arbitration community with its new approach. While offering Nigeria an opportunity to contest an overwhelmingly high penalty, it also ushers in a meticulous debate on the nature of arbitration norms and the sanctity of arbitration awards.
Implications of the Judgment on Arbitration
The implications of the P&ID judgment significantly impact the global perception of arbitration. The severe allegations concerning the corruption of arbitrators potently taint the sanctity and credibility of the arbitration process. The significance of ensuring not just the fairness of the arbitration process but its clear perception of being fair, cannot be understated. This is not without reason- it needs to be borne in mind that arbitrators are typically granted considerable powers, facilitating them to essentially ‘write the law’ in significant points of the dispute. Further, the opacity of arbitration proceedings potentially enables and conceals corrupt practices, encouraging distrust and apprehension in the institutional process of arbitration.
Learning Outcomes
The Justice Knowles’ judgment document is fast becoming a training document for many. It has also come with its learning outcomes many of which both the Nigerian State, Commercial lawyers, and the arbitration community must take a cue from. Some of them are as follows:
- Robust Due Diligence: Contracting parties must conduct thorough due diligence to assess the financial, legal, and technical capabilities of potential partners. This includes verifying the authenticity of documents and ensuring compliance with regulatory frameworks to minimize the risk of entering into agreements with unreliable or fraudulent entities. It is interesting to know that the promoters of P&ID have been doing business since the ’90s’ and no one profiled them against their acclaimed professional background.
- Anti-Corruption Measures: Governments and organizations should implement stringent anti-corruption policies and procedures to prevent corrupt practices in contract procurement. This involves promoting transparency, conducting regular audits, and enforcing penalties for violations.
- Strengthen Contractual Obligations: Parties involved in contracts should prioritize the clear and precise delineation of obligations, rights, and remedies. This includes incorporating mechanisms for dispute resolution, such as arbitration, to provide a fair and efficient means of resolving conflicts.
- Contract Management: Effective contract management is crucial to ensure compliance with contractual obligations, monitor performance, and address any potential breaches promptly. Establishing robust monitoring and reporting mechanisms can help identify and rectify issues before they escalate into costly disputes. Many of the infractions committed by the public servants were due to carelessness and weak contract management structures.
- Enforceability of Arbitration Awards: The P&ID case highlights the importance of recognizing and enforcing arbitration awards. Governments and parties to international contracts should respect the integrity and finality of arbitration decisions, as they play a vital role in resolving cross-border disputes and maintaining investor confidence.
Conclusion
Although bribery allegations featured prominently in Nigeria’s submissions on serious irregularity, the legal basis for Justice Knowles’ findings of serious irregularity was that of fraud, which is a different cause of action from that of bribery under English (or Nigerian) law. In this instance, the Court emphasized that “Section 68(2)(g) of the English Arbitration Act is concerned with the question of whether there was fraud and an award or conduct contrary to public policy’-the basis of the London Court’s conclusion. Either way, the case places a glaring spotlight on the potential corruption of arbitrators generally, pleading for increased transparency and probity in arbitration proceedings.
The judgment is also a direct challenge to the arbitration community to, as a matter of urgency, draw up an effective code of ethics of the practice of arbitration. This is the only way Users of the mechanism can continue to find it a credible one for resolving commercial disputes.
While the arbitration process aims to encourage faster and more effective dispute resolution, fostering a system that prioritizes ethical standards with zero tolerance for corruption is a quintessential prerequisite for its credibility.
TOLU ADEREMI
PARTNER, PERCHSTONE & GRAEYS, LP
LL.B (IBADAN), B.L, LL.M (ABERDEEN), DOCTORAL CANDIDATE (DTU), VISITING PROFESSOR ON ALTERNATIVE DISPUTE RESOLUTION (ADR), CHAIRMAN, INTERNATIONAL LAW ASSOCIATION ARBITRATION COMMITTEE, MEMBER, INTERNATIONAL CHAMBER OF COMMERCE (ICC) COMMISSION ON ARBITRATION, PARIS.

by Legalnaija | Nov 6, 2023 | Blawg

Introduction
In an increasingly interconnected world, the digital landscape of any nation is the beating heart of its progress, potential, and prosperity. For Nigeria, a nation teeming with promise, the digital realm represents an unparalleled opportunity to leapfrog into the future. However, like any frontier of promise, this digital landscape is not without its perils. Enter the realm of cybersecurity an omnipresent shield that guards the gates of Nigeria’s digital domain. In an age where data flows like a mighty river, and the lines between physical and virtual reality blur, the significance of cybersecurity to Nigeria cannot be overstated. It’s not merely a matter of safeguarding data; it’s about protecting the very essence of the nation’s growth, security, and resilience.
The implications ripple far and wide, transcending individual businesses and government facilities. In this article, we embark on a journey to unveil the intricate tapestry that is cybersecurity in Nigeria. From the bustling markets of Lagos to the corridors of power in Abuja, from the bustling startups in Port Harcourt to the rural heartlands, this is a story that affects us all.
As we delve into the intricate depths of this discourse, our foremost scrutiny will be directed toward the paramount role played by cybersecurity legislation in molding the nation’s economic landscape, bolstering the security of supply chains, fortifying the integrity of critical infrastructure, and upholding the sanctity of individual privacy and safety. Within this legal odyssey, we shall navigate the labyrinthine confluence of imminent threats and the unwavering resolve to withstand them, acknowledging the inherent vulnerability and cultivating robust digital bulwarks that are not only requisite but fundamental in the protection and preservation of Nigeria’s digital future.

Cybersecurity Landscape in Nigeria: An Overview
The International Telecommunications Union [ITU] defines Cybersecurity as “the collection of tools, policies, security concepts, security safeguards, guidelines, risk management approaches, actions, training, best practices, assurance and technologies that can be used to protect the cyber environment and organization and user’s assets” (Sreenu & Krishna, 2017). ITU also notes that the general objectives of Cyber Security are: Availability; Integrity, (which may include authenticity and non-repudiation), and Confidentiality. Continuous vigilance and adaptation to evolving threats are crucial in maintaining effective cybersecurity (Moreta et al., 2023). Cybersecurity practically acts as the guardian of data quality, preserving trust and the seamless flow of information while shielding against unauthorized access and manipulation. It upholds the essence of a secure digital realm.
The current cybersecurity landscape in Nigeria reflects a dynamic and evolving terrain, marked by both opportunities and challenges. As the nation embraces digital transformation and experiences rapid technological growth, it simultaneously faces heightened cyber threats and vulnerabilities. Nigeria, with its burgeoning digital economy and expanding online presence, has become a prime target for cyberattacks. These threats encompass a wide spectrum, from financially motivated attacks, such as phishing and ransomware, to politically and socially motivated incidents.
In a country where millions of Nigerians engage in daily online activities, from financial transactions to social connections and e-commerce, the digital realm has become an integral part of our lives. The delicate and often sensitive nature of these interactions underscores the critical role of cybersecurity. With online banking, e-commerce, digital communication, and remote work becoming the norm, the nation’s economic and social fabric relies on the sanctity of these digital transactions. The ramifications of a cybersecurity breach can be staggering, ranging from financial losses and personal data exposure to threats to national security. Thus, the importance of robust cybersecurity measures cannot be overstated. As Nigeria accelerates its digital transformation, including e-governance and e-health initiatives, the stakes rise higher. Ensuring the confidentiality, integrity, and availability of digital assets becomes paramount. A secure digital environment not only fosters trust and confidence but also empowers the nation to harness the full potential of the digital age.
The Cyber Security Experts Association of Nigeria (CSEAN) anticipates a gradual escalation in the incidence of cyber threats within the Nigerian landscape, where the Small and Medium Scale Enterprises (SMEs) sector is expected to bear the brunt of these adversities. As per the findings in the CSEAN report, there was an 87% surge in phishing attacks targeting SMEs in 2022, signifying a significant increase from the 37% recorded in 2021.
Cybersecurity Laws and Regulations in Nigeria: Legal Implications and Consequences
Nigeria finds itself at a crossroads where a surge in cybercrimes has reached an alarming magnitude. This multifaceted threat encompasses financial fraud, data breaches, phishing scams, and ransomware attacks. Beyond their digital confines, these perils cast a shadow over the nation’s economic stability, individual privacy, and even national security. In light of this intricate and escalating cybersecurity challenge, the imperative for legal intervention is undeniable. Legal measures must serve as a robust bulwark against the chaos and disarray that these cybercrimes can instigate. The regulatory framework should uphold the rule of law, deter cybercriminals, and ultimately secure Nigeria’s digital future and socioeconomic well-being.
Continuing from the preceding context, let us delineate several of the extant regulatory frameworks that pertain to cybersecurity in Nigeria;
- Cybercrimes (Prohibition, Prevention, Etc.) Act 2015.
- Nigeria Data Protection Regulation 2019.
- National Cybersecurity Policy and Strategy, 2021.
- Nigeria Data Protection Act 2023 (NDPA)
The Cybercrimes (Prohibition, Prevention, Etc.) Act according to its objectives provided in section 1 of the Act was created to establish an efficient and comprehensive legal and regulatory structure to address cybercrimes in Nigeria, safeguard critical national information infrastructure, and enhance cybersecurity measures, including data protection and privacy rights.
Part 3 of this Act meticulously delineates actions that qualify as offenses, along with the corresponding punitive measures prescribed for each transgression. These transgressions encompass a range of activities, including, but not restricted to: unauthorized access to computer systems, violations against critical national information infrastructure, acts of system interference, interception of electronic communications, such as messages and emails, illicit electronic fund transfers, phishing schemes, unsolicited mass emails (spam), propagation of computer viruses, and computer-related fraudulent activities. It is imperative to underscore that each of these infractions carries a unique sentencing regime, with certain egregious transgressions not affording the option of a pecuniary fine due to the gravity of their impact.
Furthermore, the statute also imposes a set of obligations upon individuals or entities engaged in the operation of computer systems or networks. Among these obligations is the compelling duty to promptly report any instances of cyberattacks or intrusions to the Computer Emergency Response Team (CERT) Coordination Center, facilitating the swift enactment of necessary remedial actions. Failure to comply with this specific duty is met with a substantial penalty of 2,000,000 naira and a seven-day suspension of internet service.
It is noteworthy that a subset of these offenses possesses a technical intricacy that necessitates the expertise of a qualified professional to ascertain whether a given action qualifies as an offense under the purview of this legislation.
The Nigeria Data Protection Act being the latest legislative framework governing the domains of data privacy and security, meticulously delineates the obligations bestowed upon data controllers and processors concerning their responsibilities to safeguard the data placed in their custody directly and indirectly by the data subjects. The legislation establishes a commission entrusted with the critical mandate of overseeing data controllers, ensuring that they do not overstep the bounds of authority granted to them by data subjects. This commission is tasked with evaluating the conduct of these data controllers to ascertain their compliance with the stipulations outlined in the Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA).
The legislation has seamlessly integrated globally recognized best practices within its provisions, particularly on the obligations and standards imposed upon data controllers in the realms of data processing, data transfer, and various other relevant facets.
The Nigeria Data Protection Regulation was not invalidated by the emergence of the NDPA. However, the Nigeria Data Protection Act (NDPA), being a primary national legislation, holds precedence over the Nigeria Data Protection Regulation (NDPR), which is categorized as subsidiary legislation. Importantly, it is crucial to note that the NDPA, while exerting its legal authority, does not nullify or revoke the NDPR. Rather, the NDPA explicitly stipulates that all regulations promulgated by the National Information Technology Development Agency (NITDA), encompassing the NDPR, maintain their legal validity and remain in effect, as though they were originated or endorsed by the Nigeria Data Protection Commission (NDPC).
The National Cybersecurity Policy and Strategy, The policy document embodies a comprehensive and adaptable framework, placing significant emphasis on the collaboration between the government, the private sector, and citizens to safeguard digital ecosystems. Nigeria aspires to cultivate strong legal and regulatory frameworks that can effectively combat cybercrime, fortify the protection of critical infrastructure, and ensure the privacy of data. This endeavor seeks to be accomplished through the persistent monitoring of cyber threats, the development of incident response plans, and the implementation of public awareness campaigns, all of which are pivotal components aimed at nurturing a resilient cyber landscape conducive to sustainable growth and the secure advancement of digital transformation.
Common Cyber Threats in Nigeria
In the digital age, the pervasive nature of cyber threats casts a daunting shadow over our interconnected world. The dangers are manifold, ranging from data breaches and financial fraud to critical infrastructure disruptions and even threats to national security. What fuels this digital menace is a complex interplay of factors, including the ever-evolving sophistication of cybercriminals, the lucrative nature of cybercrime, and the relative anonymity provided by the digital realm.
While the digital landscape offers boundless opportunities, it also harbors threats that thrive in the nation’s evolving cyberspace. Reports of phishing scams, online fraud, and data breaches paint a picture of a thriving cyber underworld. The reasons behind this growth include a lack of comprehensive cybersecurity infrastructure, limited awareness, and a need for robust regulatory frameworks. Understanding the dynamics of these threats is paramount, for it is only through this understanding that we can hope to fortify our defenses and ensure a secure digital future in Nigeria. Here are some of the prevalent cyber threats wreaking havoc in Nigeria:
- Phishing Attacks
- Ransomware
- Business Email Compromise (BEC)
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Attacks
- Identity Theft
- Malware Infections
- Online Fraud
- Data Breaches
- Insider Threats
- Social Engineering Scams
These threats collectively pose significant challenges to cybersecurity within the nation, thriving on the unsuspecting and the unprepared. These threats each with distinct characteristics and potential ramifications. Phishing attacks cunningly manipulate human psychology, tricking individuals into divulging sensitive information or falling prey to malicious links. Ransomware, the merciless extortionist, encrypts vital data, demanding cryptocurrency payments for its release. Business Email Compromise (BEC) infiltrates corporate email accounts to initiate fraudulent transactions or financial manipulations, while Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) assaults inundate digital services with traffic, rendering them inaccessible. Identity theft is the stealthy theft of personal information, which can lead to financial ruin and reputation damage. Malware infections propagate malicious software, compromising security, and spreading chaos. Online fraud schemes perpetrate scams and deception for financial gain. Data breaches compromise confidentiality, often exposing private data to unscrupulous entities. Insider threats arise from within an organization, posing risks to its assets. Social engineering scams craftily manipulate victims into revealing confidential information.
In 2020, Nigeria secured an unfortunate 16th place in the global ranking of countries most severely impacted by cybercrime. A recent development within Nigeria’s cyber threat landscape has unveiled a rather alarming trend: hackers are strategically enticing employees of Nigerian organizations to act as insider threats. Revelatory research indicates that these hackers are offering financial incentives to employees in exchange for access to sensitive information within an organization’s network. While specific instances of staff succumbing to such temptation were not documented, this emerging scenario is undeniably a cause for growing concern. The third quarter of 2022 bore witness to a staggering 1616% surge in data breaches in Nigeria, escalating from 35,472 incidents in the second quarter to a daunting 608,765 occurrences in the third. This unnerving spike signals a pressing need for enhanced cybersecurity measures. In a commendable stance against cybercrime, Nigeria’s Economic and Financial Crimes Commission (EFCC) has undertaken a proactive campaign in 2022, successfully convicting 2,847 individuals involved in cyber-related crimes. This marks a significant stride in the fight against cybercriminals who threaten the nation’s digital landscape and the security of its citizens.
Safeguarding Digital Assets: Best Practices
In a digital landscape fraught with risks and vulnerabilities, the need to adopt cybersecurity best practices has never been more pressing. Healthcare and financial organizations, in particular, find themselves squarely in the crosshairs of cyber threats. To safeguard sensitive data, financial assets, and the trust of their clients, individuals, and entities in these sectors must embrace the proactive measures explored in this section.
- Detecting External Security Flaws: Cybercriminals frequently zero in on organizations lacking robust security protocols, and healthcare and financial institutions are prime targets due to various vulnerabilities. In healthcare, the extensive array of internal systems often remains unpatched, granting cybercriminals easy access. Limited IT resources compound the problem, resulting in outdated security protocols. Furthermore, inadequately secured healthcare member portals can expose patient data to potential breaches. Financial service sectors encounter similar challenges as they modernize their infrastructure, transitioning from legacy systems to digital platforms. During this transition, cybersecurity gaps may inadvertently open doors for malicious actors. Criminals strategically target financial institutions, well aware of their capacity to meet ransomware demands, making them high-value targets in the digital realm.
- Conducting Penetration Tests: Penetration testing is a proactive approach employed by companies to uncover potential security vulnerabilities. By emulating hacker tactics, this method aims to detect and address security weaknesses before they can be exploited. Simulated cyberattacks are designed to exploit existing vulnerabilities, providing valuable insights to fortify defenses and protect sensitive data.
In the healthcare sector, adherence to HIPAA guidelines necessitates robust testing to ward off potential breaches. Similarly, financial institutions must follow government regulations for safeguarding consumer data. In both cases, IT teams play a crucial role in identifying and addressing security system vulnerabilities through comprehensive testing.
- Risk Prioritization Based on Business Impact: After identifying vulnerabilities in your assets, the next crucial step is to prioritize them according to the potential risks they pose to your organization. This prioritization process guides your efforts in enhancing security and establishes benchmarks for future assessments. To streamline this process, security ratings come into play. These ratings assign a letter grade to your security posture, reflecting how effectively it safeguards vital data and information. This grading system offers clarity, highlighting areas that demand immediate attention within your security framework. Additionally, these ratings prove valuable in third-party risk management, showcasing your commitment to due diligence during vendor onboarding and ongoing monitoring.
- Utilize Automated Cybersecurity Solutions: Incorporating automation into your corporate network environment plays a pivotal role in risk reduction and security enhancement. Automated cybersecurity solutions prove invaluable in network monitoring, offering IT teams the gift of time to concentrate on addressing high-risk threats.
Moreover, these automated solutions excel in reducing incident response times and swiftly curbing the propagation of attacks across networks. When appropriately configured, automated resources can extend their capabilities to assess security metrics. It is highly advisable to focus on metrics conducive to the automated gathering of data for comprehensive cybersecurity management.
- Stay Current with Regular Updates: Staying at the forefront of cybersecurity defense mechanisms is essential to ensure your security remains resilient. Regular updates and modifications are indispensable, as they empower IT teams to adapt to evolving security technology and emerging threats promptly.
- Develop an Effective Incident Response Plan: Preparedness is key in cybersecurity. An incident response plan, including dedicated teams and action checklists, minimizes harm and enables a swift recovery. The plan’s complexity varies with the attack and organization size. Regularly update and rehearse the plan for optimal performance and adaptability in the face of evolving cyber threats.
Safeguarding digital assets is an ongoing endeavor, necessitating the expertise of adaptable and continuously learning security professionals. As the threat landscape constantly evolves, these individuals must remain at the forefront of emerging trends, ensuring they are well-equipped to thwart even the most sophisticated cyberattacks. The resilience of organizations, the protection of sensitive data, and the preservation of trust in the digital age hinges upon the dedication and vigilance of such security experts.
Conclusion
The realm of cybersecurity in Nigeria stands at a critical juncture. While existing laws make strides in addressing cyber threats, more stringent measures are imperative to deter the audacity of cybercriminals and bullies. The role of legislation extends to ensuring the unwavering adherence of organizations, particularly public entities, to robust cybersecurity best practices. With public organizations safeguarding highly sensitive data, their commitment to data protection is not just an obligation; it is a covenant of trust with the public they serve. The future of cybersecurity in Nigeria hinges on the unwavering resolve of lawmakers and organizations to fortify digital defenses, guaranteeing the resilience and integrity of our digital landscape.











 Olamide Oyetayo
Olamide Oyetayo








